Science Advances | Research Article: Non–steady state thermometry with optical diffraction tomography
Label-free thermometry is a pivotal tool for many disciplines. However, most current approaches are only suitable for planar heat sources in steady state, thereby restricting the range of systems that can be reliably studied. Here, we introduce pump probe–based optical diffraction tomography (ODT) as a method to map temperature precisely
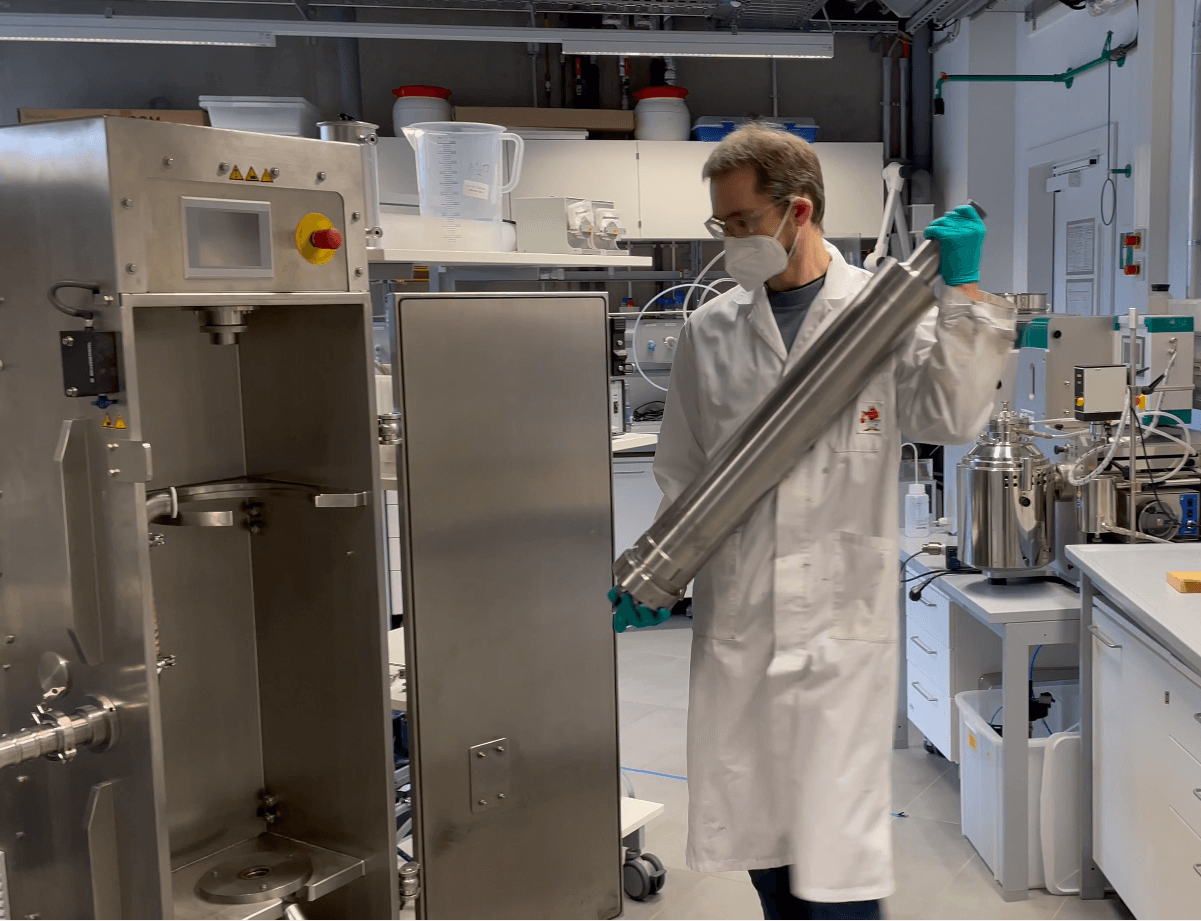
Lab exchange: “transfer of lab-scale syntheses to a larger scale”
Lab exchange: "transfer of lab-scale syntheses to a larger scale". A total profit for SPOTLIGHT. Within the SPOTLIGHT project, TNO develops lab-scale wet-chemical syntheses of plasmonic catalysts and analyses their performance in in catalytic processes. Fraunhofer is responsible for the upscaling of the developed lab-scale to large batch syntheses (up to
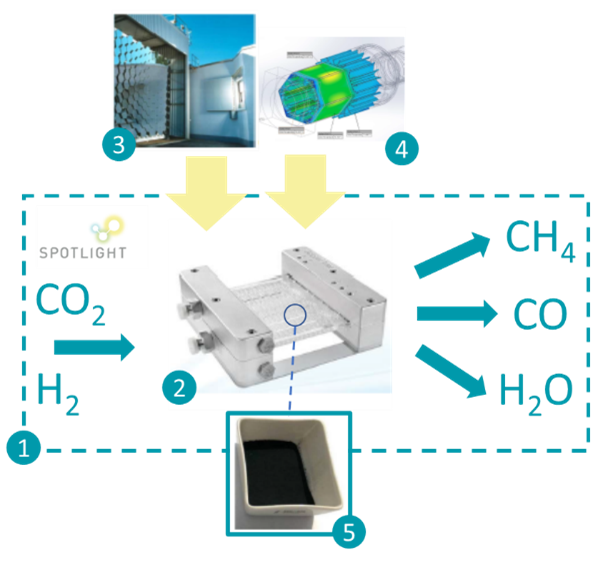
A reactor equipped with a plasmonic catalyst to produce either methane or carbon monoxide is being developed for operation under concentrated sunlight
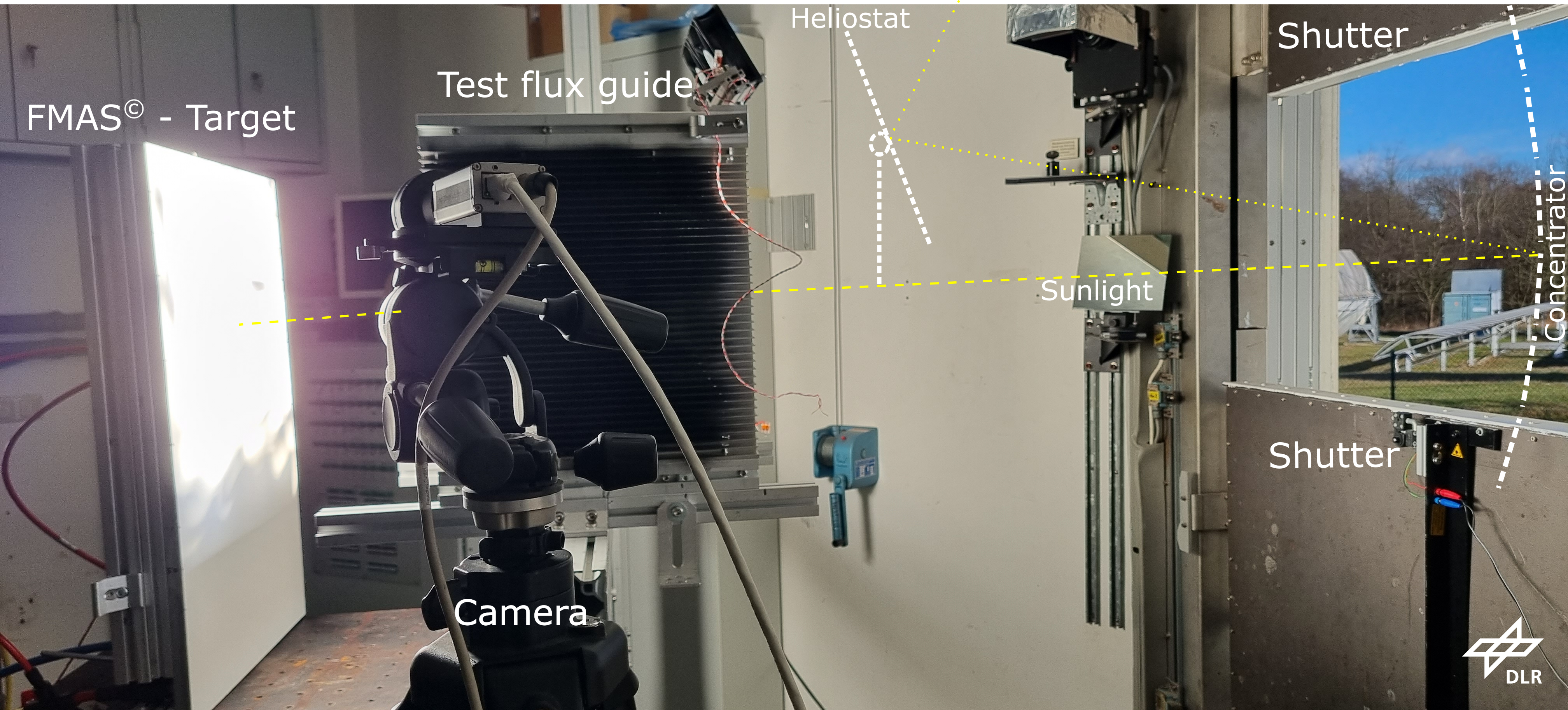
In the SPOTLIGHT project, a reactor equipped with a plasmonic catalyst to produce either methane or carbon monoxide is being developed for operation under concentrated sunlight. The SPOTLIGHT consortium will test a prototype in the solar furnace at DLR in Cologne, Germany. Here, a heliostat reflects sunlight upon a concentrator, which
AZoOptics speaks to Nicole Meulendijks from TNO about the SPOTLIGHT consortium and its use of sunlight and photonics
In this project, we are developing technologies that attribute to the safeguarding of our future energy supply by the transfer from fossil fuels to sustainable energy sources and the reduction of CO2 emissions in order to reach the objectives of the Paris climate agreement; limiting global warming to a maximum
Using Fiber Bragg Grating Sensors to Quantify TemperatureNon-Uniformities in Plasmonic Catalyst Beds under Illumination
Distinguishing between photothermal and non-thermal contributions is essential in plasmon catalysis. Use of a tailored optical temperature sensor based on fiber Bragg gratings enabled us to obtain an accurate temperature map of an illuminated plasmonic catalyst bed with high spatiotemporal resolution.Its importance for quantification of the photothermal and non-thermal contributions
The project encourages the collaboration of external stakeholders belonging to the solar fuels value of chain.
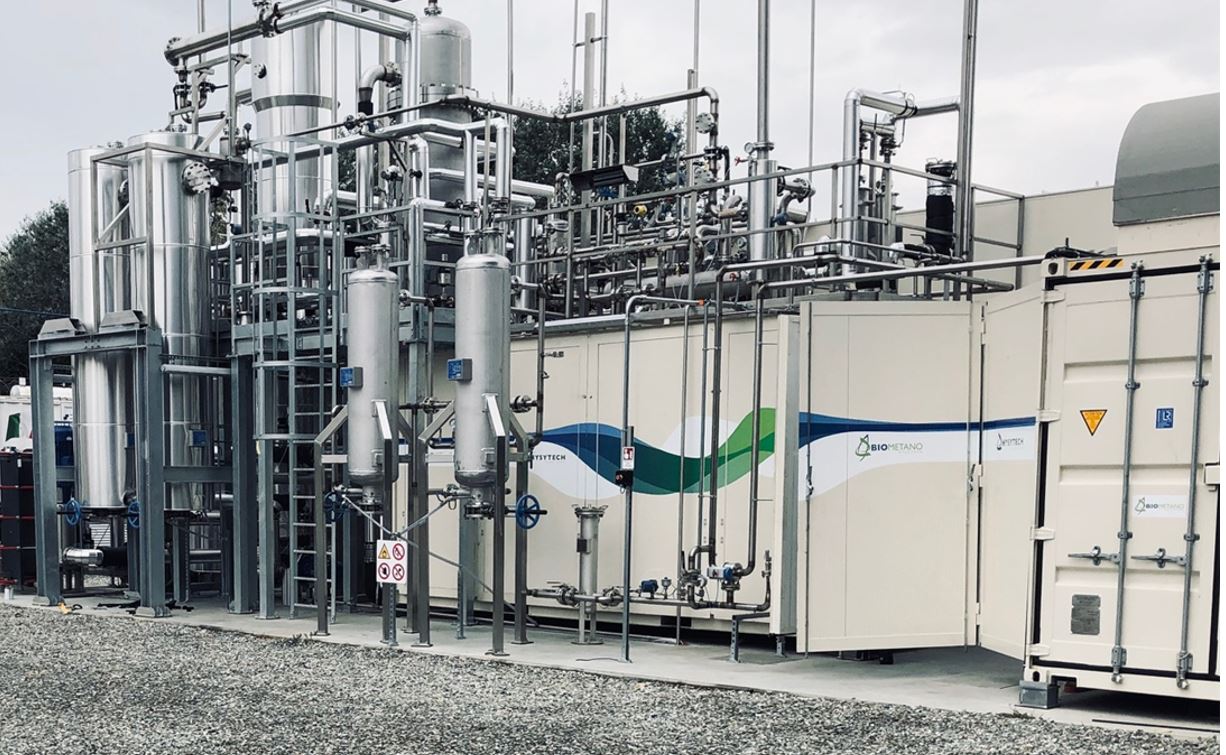
This new H2020 project that will develop innovative photonic devices for highly efficient, sunlight-fueled chemical processes. The projects aims at demonstrating an innovative process for the production of solar fuels, where the photonic device will facilitate efficient sunlight-powered conversion of CO2 and green H2 to the chemical fuel CH4 (Sabatier
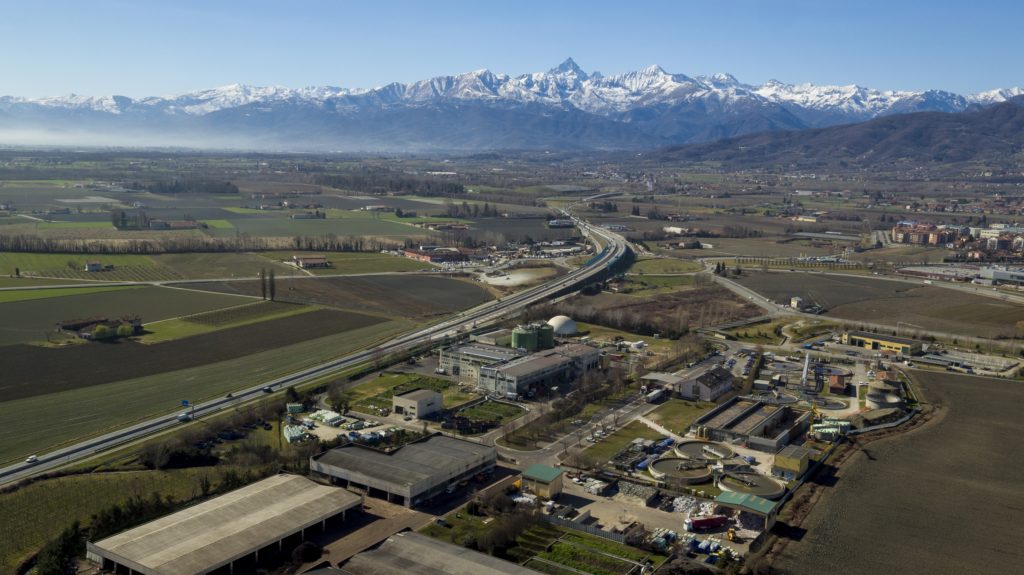
SPOTLIGHT represents for ACEA the possibility to give value to the CO2 produced by the biomethane plant
ACEA is a public multi-utility company, providing services in the water, energy and environmental sectors, the reference point at a regional level for the organic waste treatment. The ACEA Waste Treatment Plant was established in 2003 to initially serve only the Pinerolo area (150˙000 inhabitants). Currently, the organic waste treatment line is
Working together on the basic components of the photonic device to reach the overall goals
Over the last months, the Spotlight consortium has been working on the basic components of the photonic device and the overall process. During mostly online meetings, experts from the involved partners exchanged ideas in how to reach the overall goals of Spotlight with greatest impact. The topics reviewed span from
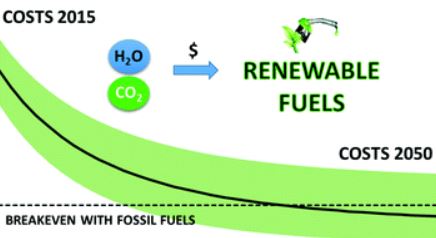
The future of solar fuels: when could they become competitive?
Solar energy driven processes with H2O and CO2 as basic feedstocks can produce “solar fuels” that could substitute their fossil based counterparts. This article summarizes the main findings of a techno-economic analysis of systems that can generate different types of fuels with renewable energy as starting point. These “renewable fuels”
New Study: Global Energy System based on 100% Renewable Energy
The new study by the Energy Watch Group and LUT University is the first of its kind to outline a 1.5°C scenario with a cost-effective, cross-sectoral, technology-rich global 100% renewable energy system that does not build on negative CO2 emission technologies. The scientific modelling study simulates a total global energy