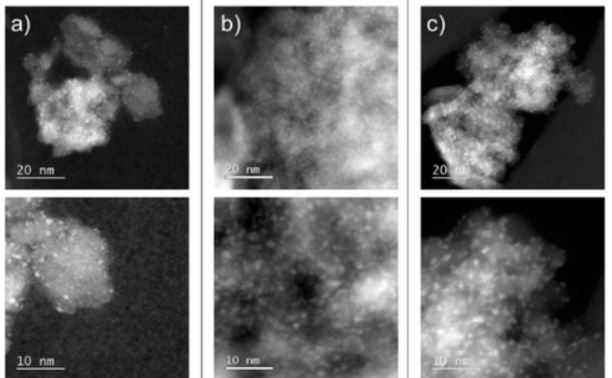
Collective photothermal effect of Al2O3-supported spheroidal plasmonic Ru nanoparticle catalysts in the sunlight-powered Sabatier reaction
Plasmon catalysis is an interesting technology concept for powering chemical processes with light. Here, we report the use of various Al2O3-supported Ru spheroidal nanoparticles as catalyst for the low-temperature conversion of CO2 and H2 to CH4 (Sabatier reaction), using sunlight as energy source. At high loadings of Ru spheroidal nanoparticles
A Study on the Contribution of Laser Illumination
The interaction between plasmonic metal catalysts and visible light can be exploited to increase their catalytic activity. This activity increase results from the generation of hot charge carriers or hot surfaces, or a combination of both. We have studied the light-induced Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reaction of bromobenzene and m-tolylboronic acid using
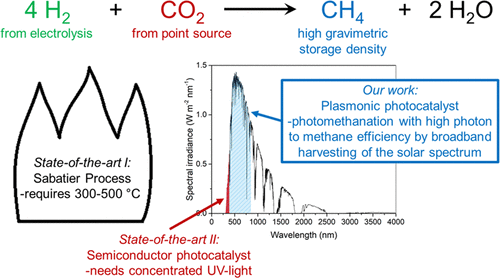
Sunlight-Fueled, Low-Temperature Ru-Catalyzed Conversion of CO2 and H2 to CH4 with a High Photon-to-Methane Efficiency
Methane, which has a high energy storage density and is safely stored and transported in our existing infrastructure, can be produced through conversion of the undesired energy carrier H2 with CO2. Methane production with standard transition-metal catalysts requires high-temperature activation (300–500 °C). Alternatively, semiconductor metal oxide photocatalysts can be used,